One effective method is the DIR/Floortime approach. This intervention uses a holistic approach and has been proven to progress a child’s skills across areas of communication, emotional functioning, daily living skills, and parent-child interactions.
DIR stands for Developmental, Individual-differences, Relationship-based, and is sometimes referred to as DIR/Floortime, or simply Floortime. The approach was initially developed by the psychiatrist Dr. Stanley Greenspan in the 1980s. It combines principles of human development with findings about sensory and motor development.
Understanding DIR/Floortime
- Developmental: This component acknowledges the developmental stages that children go through, considering their individual progress within these stages.
- Individual Differences: This aspect recognizes and respects each child’s unique qualities, strengths, and challenges. DIR aims to customize a child’s intervention plan based on their individual needs, rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Relationship-Based: According to DIR/Floortime, relationships fuel our development. The approach follows the belief that positive relationships with the child’s caregivers and others play a critical role in the child’s development. It’s believed that building strong emotional connections is essential for forming a foundation for growth.
The DIR/Floortime model is considered child-led. Therapists, parents, and caregivers follow the child’s lead, which can help promote a sense of empowerment and encourage the child to actively participate in therapy.
Core Principles
- Follow the Child’s Lead. Therapists and caregivers engage in activities that capture the child’s interests. This can create a supportive, positive environment for interaction.
- Challenge at the Right Level. Children are challenged within the “Zone of Proximal Development”, a place where a skill is too difficult for the child to complete independently, but can be successfully completed with the support and guidance from another individual.
- Use Scaffolding to Support the Child. Scaffolding is a technique used to teach new developmental skills. It involves supporting a child by providing just enough assistance to allow him or her to be successful at completing a task. Working with a child within the Zone of Proximal Development and using scaffolding can ensure activities are enjoyable and conducive to growth.
- Incorporate Emotional Interactions. Therapists and parents engage in emotionally meaningful interactions with the child. This can foster a sense of trust and security with these individuals.
- Expand Circles of Communication. The therapist and parents encourage a child to use gestures, words or other means of communication to enhance their ability to connect with others.
- Develop Symbolic Thinking. Symbolic thinking is seen as a significant part of a child’s cognitive development. Caregivers and therapists work to help a child develop their capacity for imagination and abstract thinking through play.
Who Can Benefit from DIR/Floortime
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): DIR/Floortime is known for its use with Autistic children. Research has shown that Autistic children can make substantial progress in different levels of functioning through the use of Floortime.
- Sensory Processing Disorders: Sensory-rich experiences provided through therapy, such as Occupational Therapy, using DIR/Floortime principles can help children develop a better understanding and regulation of sensory input.
- Speech and Language Delays: Services such as Speech Therapy that follows the DIR/Floortime method focuses on expanding circles of communication to support children with speech and language delays. Therapists and parents can facilitate growth in a child’s expressive and receptive language skills through meaningful interactions and play.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Challenges with attention and hyperactivity can be addressed through the use of engagement and individualized support within the DIR/Floortime model.
How Does DIR/Floortime Compare to ABA?
Both approaches aim to promote positive development of skills, the philosophies, methods, and goals of the approaches differ.
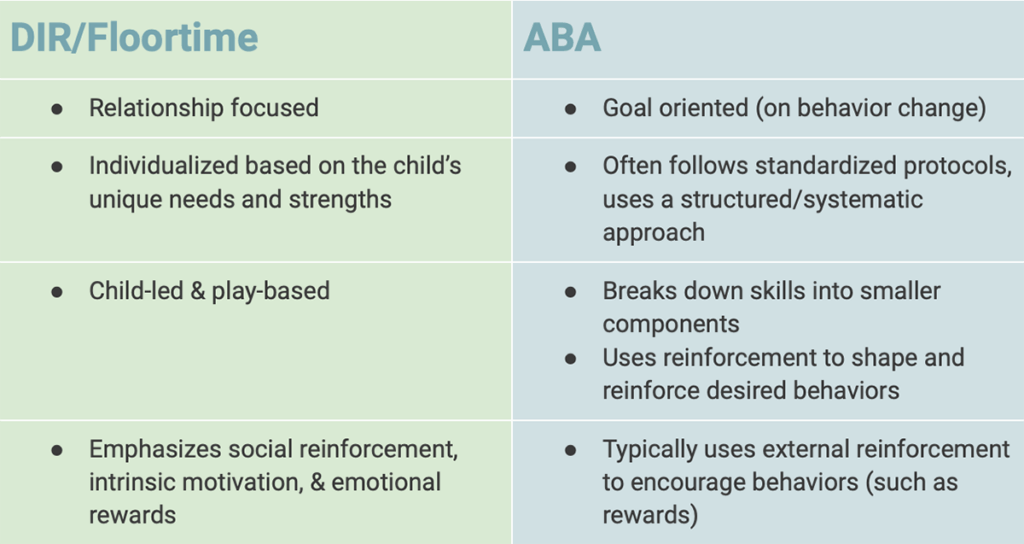
Which approach is more effective? Both the DIR/Floortime method and ABA have been shown by research to effectively improve developmental skills in children with diagnoses such as Autism.
When choosing what approach to use with their child, parents should consider the individual needs and learning style of their child, their own preferences in teaching methods, and the expertise of the professionals working with the child.
Additional Resources
TherapyWorks offers speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, in which therapists incorporate principles of DIR/Floortime. TherapyWorks also offers ABA, another effective approach to improving a child’s developmental skills. If you would like to learn more or discuss your child’s specific needs, please don’t hesitate to reach out to TherapyWorks!




